▣ What Is “Perceived Temperature”?
.
Perceived temperature refers to the temperature that people actually feel, which takes into account not only the air temperature but also factors such as wind and humidity.
.
In other words, even if the air temperature is the same, stronger winds or higher humidity can make it feel colder or hotter. Perceived temperature expresses this difference as a measurable value.
.
In summer, it is typically determined by considering both air temperature and humidity. Humidity plays a key role because when it is high, sweat evaporates less efficiently, reducing the body’s ability to release heat—thereby increasing the risk of heat-related illnesses.
.
.
.
▣ Concept of Perceived Temperature
| Actual temperature | The air temperature measured with a thermometer. |
| Perceived temperature | The temperature felt by the human body, taking into account the effects of wind and humidity |
.
▣ Calculating Perceived Temperature
.
1) Summer perceived temperature – Calculated using air temperature and humidity (e.g., Heat Index)
2) Winter perceived temperature – Calculated using wind speed and air temperature (e.g., formulas used by Environment Canada)

.
▣ Perceived Temperature and Health
.
- High perceived temperature – Increases the risk of heatstroke, dehydration, and cardiovascular problems.
-
Low perceived temperature – Increases the risk of frostbite and hypothermia..
.
▣ Heat Index
The heat index is a measurement used to estimate how hot it feels by combining air temperature and humidity.
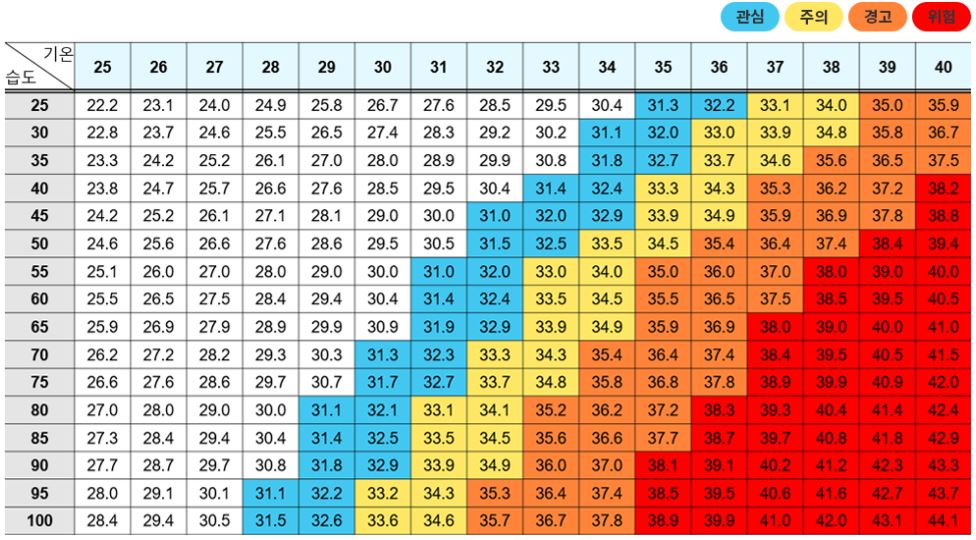
.
▣ Factors Affecting Perceived Temperature
.
1) Summer: Humidity
- When humidity is high, sweat evaporates less efficiently, making it feel hotter and more uncomfortable.
- Example: At 33 °C with humidity above 80%, the perceived temperature can exceed 40 °C.
.
2) Winter: Wind
- Wind increases heat loss from the skin, making it feel colder.
- Example: Even if the air temperature is 0 °C, strong winds can make it feel like –10 °C or colder.
.
