From 2019 to 2023, there were 9 fatal accidents related to deck plate collapse, resulting in 15 worker deaths. Although these accidents are not frequent, when they do occur, they often result in the simultaneous deaths of two or three workers — making preventive safety measures essential for ensuring safe work conditions.

_
What Is a Deck Plate??
Formwork and supports (falsework) are temporary structures installed to maintain the shape of concrete structures and to support dead loads and working loads until the concrete reaches its design strength. These supports can be divided into column-type and beam-type..
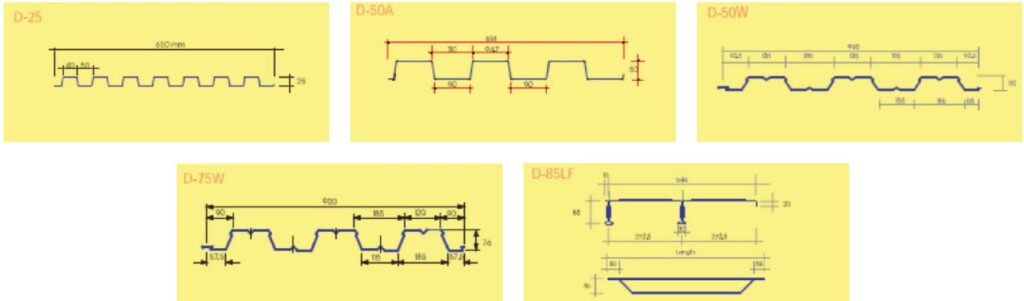
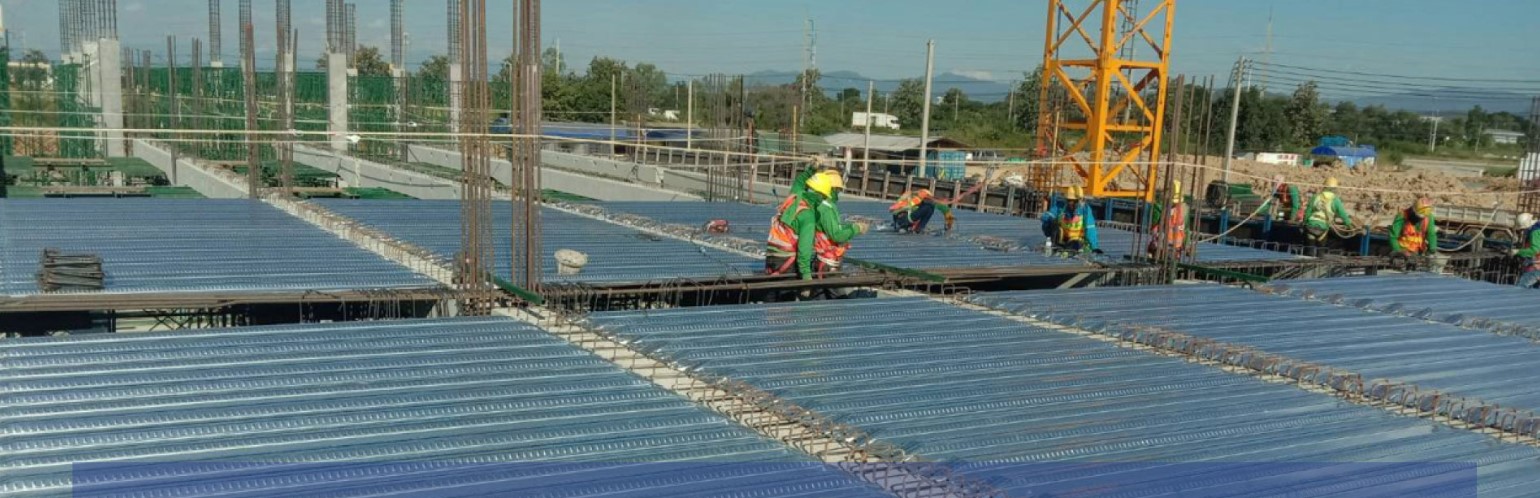
‘A deck plate (also known as a steel deck) is a corrugated or pressed steel plate made from galvanized sheet or steel wire. It serves both as a floor form for concrete slabs and as a beam-type support..
Beam-type supports reduce or eliminate the need for vertical columns beneath the floor, making them ideal for high-rise buildings, civil structures like bridges, and logistics centers with tall ceilings.
.
.
_
Preventive Measures During Deck Plate Installation
1. Prepare and Follow Design Documents
Before installing formwork and supports, including deck plates, a construction work plan and detailed assembly drawings must be prepared in advance. A structural review by a qualified expert should always precede the preparation of these drawings.
Materials like steel decks must comply with the Korean Industrial Standards (KS) or equivalent specifications. The drawings must include material type, cross-sectional dimensions, installation spacing, and connection methods. These should be reviewed during the daily safety meeting and key safety precautions should be communicated to workers through a toolbox meeting (TBM) before work begins.
2. Secure Both Ends of the Deck Plate Properly
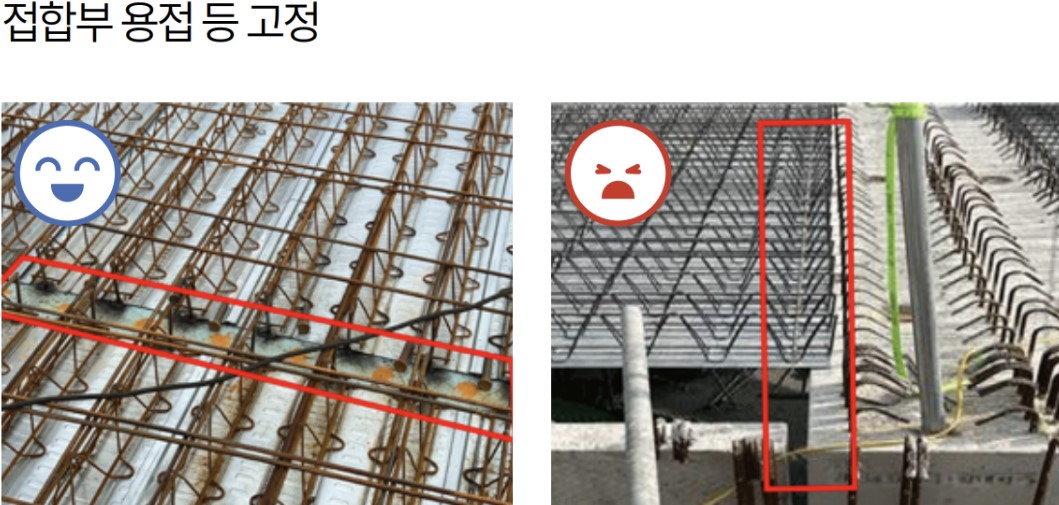
To prevent the deck plate from slipping or detaching from the steel beams or beam side forms, both ends must be properly supported and secured using nails, welding, or other methods.
The bearing length must meet structural review results or the manufacturer’s guidelines, reflecting the structure’s size and characteristics. For steel structures, the minimum bearing length is 50mm in the rib direction and 30mm in the width direction.


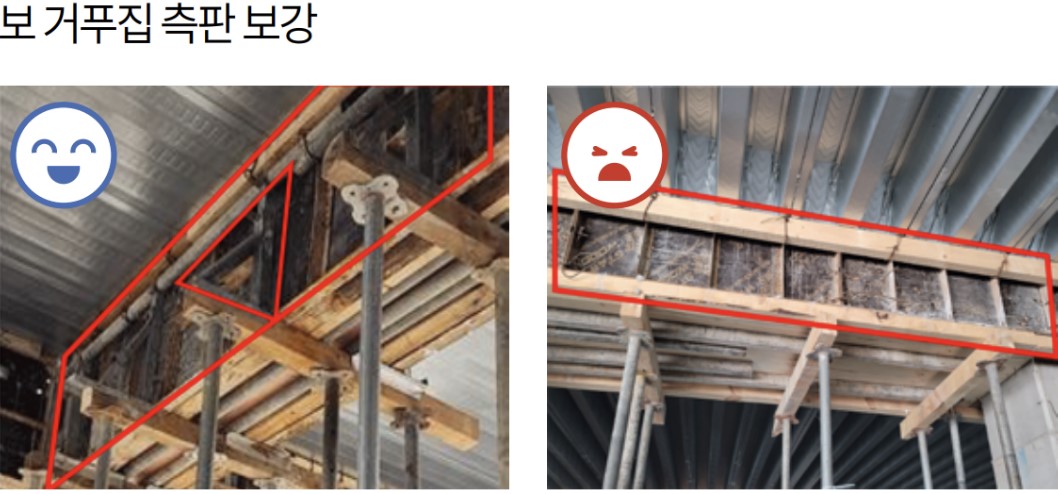
3. Reinforce with Additional Supports
Deck plates installed on beam side forms in reinforced concrete structures are subjected to material loads, work loads, and concrete placement loads. These can cause side forms to bulge or topple.
Reinforcement is essential — ideally with multiple measures:
❶Add Vertical Supports Under the Center of Deck Plates
Installing vertical props under deck plates distributes the concrete load and reduces the additional stress and deflection on both the form and deck plate. In multi-story structures, however, added loads may transfer to lower floors, risking overload. In such cases, props should be installed continuously down three levels or structural review should confirm the need to retain or remove them.
_
❷ Add Vertical Supports Adjacent to Beam Side Forms
In buildings with high ceilings, such as logistics warehouses using system supports, vertical props can be installed beneath the deck plate near the beam formwork.
_
❸ Install Brackets or Horizontal Supports to Prevent Form Spread
If vertical props under the deck plate are difficult to install, horizontal supports or brackets should be placed between the beam forms to prevent side expansion or tipping..
_
❹ Install Horizontal Braces Between Vertical Props
Installing horizontal braces between props supporting the beam forms integrates the lower structure, helping resist horizontal loads from vibration or impact during work. It also prevents buckling — a sudden failure due to axial compression on long vertical members..
* Buckling: a form of structural failure where a slender vertical element suddenly bends or collapses under compressive stress, even if it hasn’t reached its strength limit.




Preventing Collapse During Concrete Pouring
❶Plan, Inspect, and Share Concrete Pouring Schedule
Concrete pouring must follow a detailed plan based on site conditions, weather, structural analysis, and the formwork drawings. This plan must be reviewed during daily safety meetings and communicated to workers via TBM. On the day of the pour, inspect for any deformation or ground settlement under the forms. Proceed only after repairs if needed.
❷Follow Pouring Sequence and Thickness Guidelines
Comply with the planned pouring thickness and follow the structural analysis. Concrete should be placed gradually and evenly to avoid creating eccentric loads, which can deform the formwork or dislodge supports, causing collapse..
_
❸Assign Watch Personnel and Evacuation Plans
During pouring, assign watch personnel to monitor for deformation or sinking. If signs of collapse are detected, stop work immediately and evacuate workers. Resume only after reinforcement.
_ _
❹ Observe Proper Curing Time
Do not dismantle formwork or supports until the concrete has cured per the specifications. Removal timing depends on cement type, concrete mix, structural importance, load, and temperature. If compressive strength tests are not conducted, follow standard curing durations and retain props in multi-story structures for at least three levels, including the poured floor..
Source: Korea Occupational Safety and Health Agency (KOSHA)