▣ Impact Force Without a Seatbelt
.
.
▣ Principle of Calculation
.
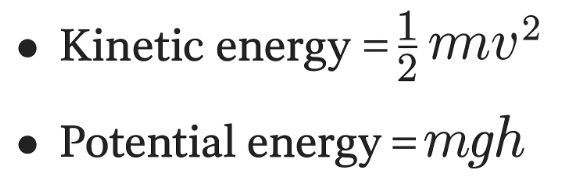
.
If we set the two energies equal, the mass m cancels out.
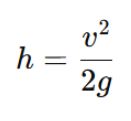
Here, v is velocity (m/s), and g = 9.81 m/s².
.
Unit conversion for speed:
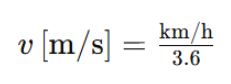
.
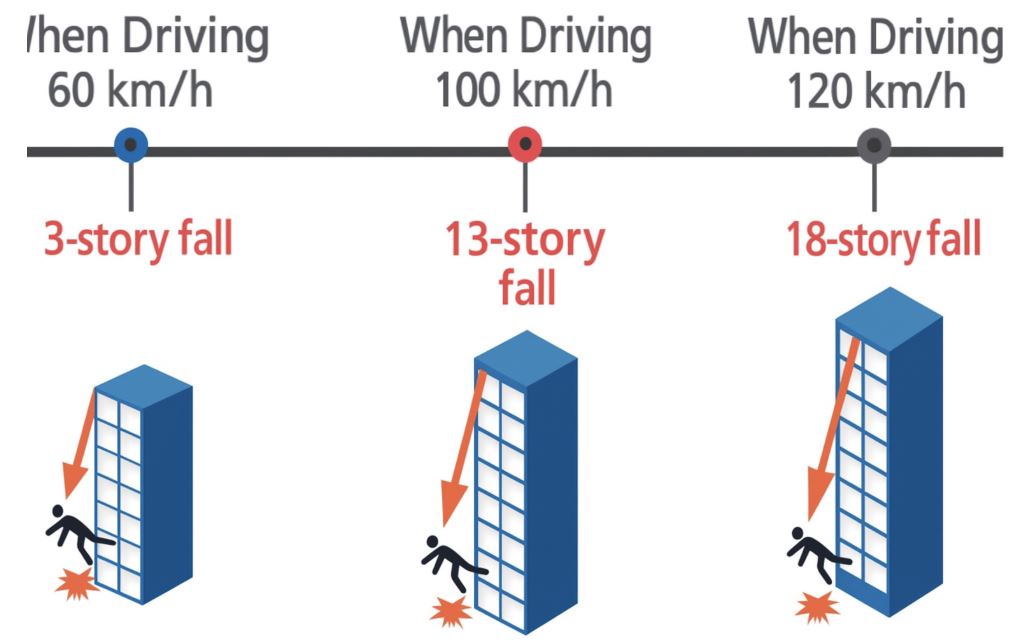
Speed Converted to Equivalent Height (assuming one floor = 3.0 m)
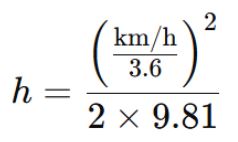
.
| Driving Speed | Equivalent Height (h) | Equivalent Floors (3 m/floor) |
|---|---|---|
| 60 km/h | 14.16 m | About 4.7 floors |
| 100 km/h | 39.34 m | About 13.1 floors |
| 120 km/h | 56.65 m | About 18.9 floors |
.
.
▣ Seatbelts and “Impact”
While energy (equivalent height/floors) depends on speed, the real factor that determines injury risk is the deceleration distance.
-
Without a seatbelt: The body collides with the dashboard or windshield and stops within just a few centimeters → extremely high impact force.
-
With a seatbelt: The belt stretches, the pretensioner activates, and the airbag deploys, increasing the deceleration distance to several tens of centimeters → dramatically reducing the impact force.
In short, even at the same speed, wearing a seatbelt drastically lowers the maximum impact your body experiences.
.
.
▣ Proper Way to Wear a Seatbelt

.
