전기 사용에 있어서 가장 위험한 점은 무엇일까요?
개인적으로 에너지라는 막연한 단어에 들어있는
무색/무취라고 생각합니다.
만져지지 않고,
보이지 않으며,
냄새도 없는 에너지라는 점이죠!!
잘못 사용된 에너지가 우리 안전의 치명적인 위험요인이 될 수 있습니다.
아래는 전기안전교육 자료입니다.
일반 근로자를 대상으로 작성하여 교육자료로 바로 사용이 가능할 것 입니다.
[Contents]
[Electrocution Statistics]
- About 5 workers are electrocuted every week
- Causes 12% of young worker workplace deaths
- Takes very little electricity to cause harm
- Significant risk of causing fires
- The most potential area of Risk
- Second leading cause of death in construction

[Electrical Definition]

[Mishap Outcomes]
Burns
Electrocution
Shocks
Arc Flash / Arc Blast
Fire
Explosions
[Common Direct Causes]

[Common Indirect Causes]

[Burns]

[Electrocution & Shock]
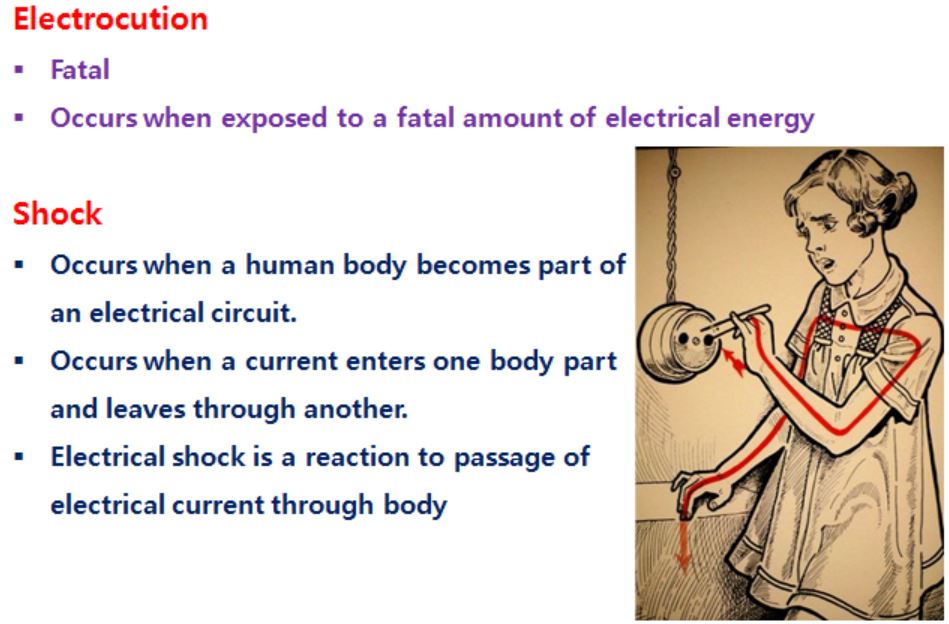
[Electrical Shock]
Dangers of Electical Shock
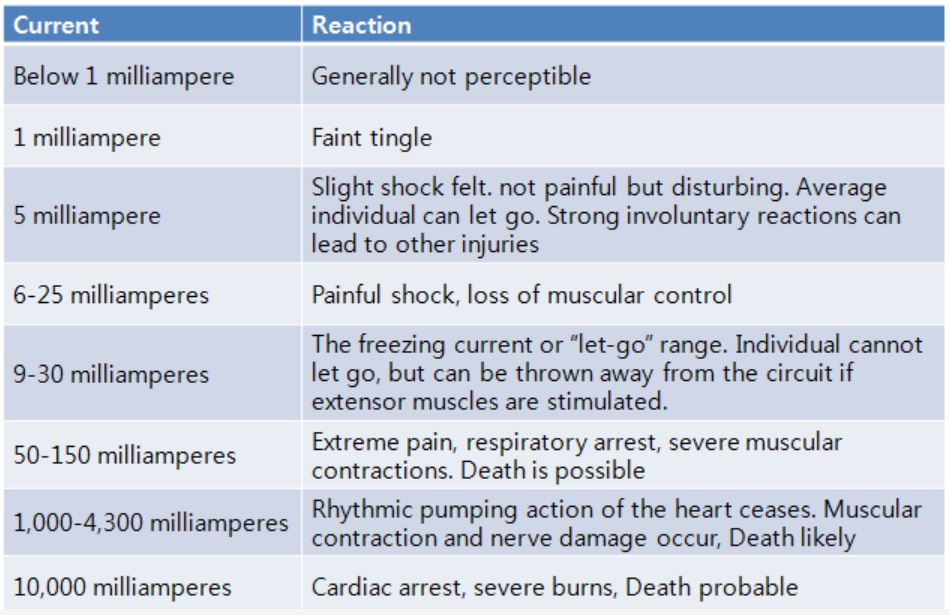
- Currents greater than 75 mA can cause ventricular fibrillation
- Will cause death in a few minutes unless a defibrillator is used
- 74 mA is not much current – a small power drill uses 30 times as much
[Electrical Shock Chart]
[Arc Flash/Blast]


[Fire & Explosion]

[Qualified Personnel]
Electrical work shall be performed by Qualified Personnel
with verifiable credentials who are familiar
with applicable code requirement

[Controlling Electrical Hazards]
Organization uses various methods to protect
all people involved from hazards associated with electricity

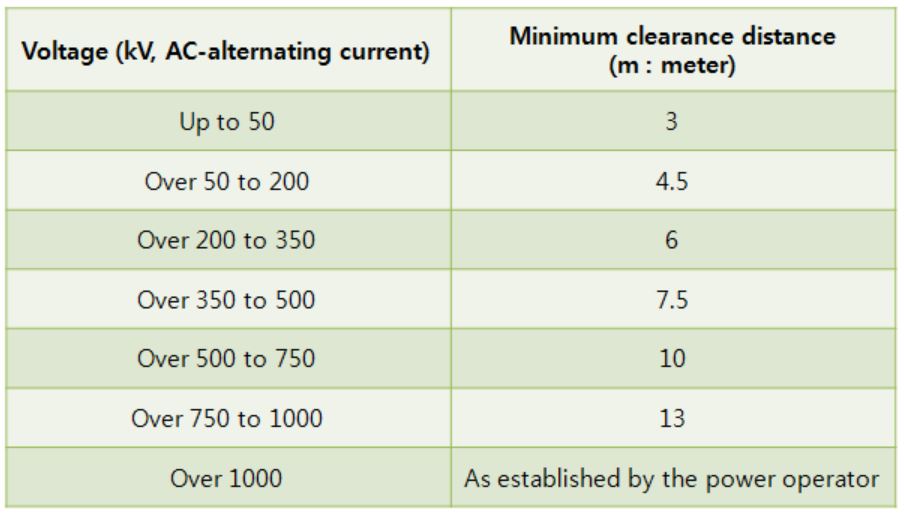
[Safety Distance]
Commonly used with regard to power lines
[Isolation & Guarding]

[Enclosure of electrical parts]
A major concept of electrical wiring in general, e.g.,
all connections are made in a box
[Grounding]
- Required for all non-current carrying exposed metal parts, unless isolated or guarded as above
- All electrical circuits, equipment and enclosures shall be grounded to provide a permanent, continuous, and effective path to ground
- Corded tools may be either grounded or be double-insulated

[Insulation]
- Intact insulation allows safe handling of everyday electrical equipment, including corded tools. Category also includes insulated mats and sleeves

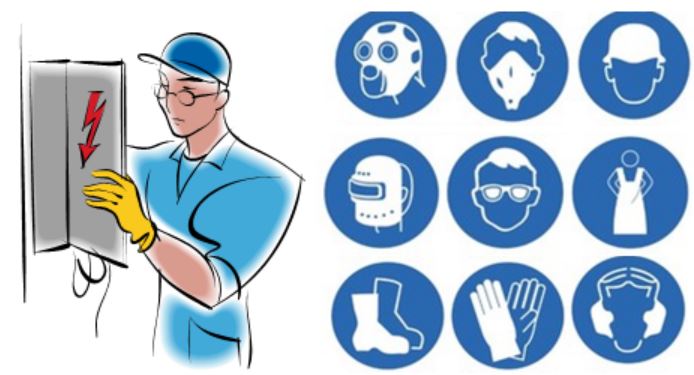
[PPE]
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Using insulated gloves and other apparel to work on energized equipment, limited to qualified and trained personnel working under very limited circumstances
[Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter]
GFCI
All receptacle outlets that provide temporary electrical power during construction, maintenance, repair, or demolition shall have GFCI protection for personnel

[Testing GFCI’s]

[Lock out / Tag out Procedures]
- Identify sources of electrical energy for equipment/circuits in question
- Disable backup energy sources
- Identify shut-offs for each energy source
- Notify all personnel that equipment and circuitry must be shut off, locked out, and tagged out


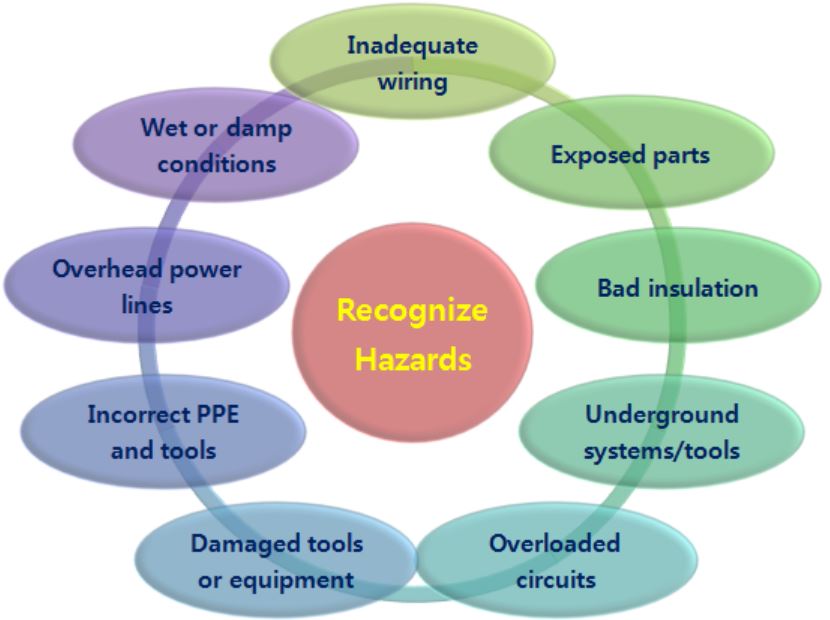
[Recognize Hazards]
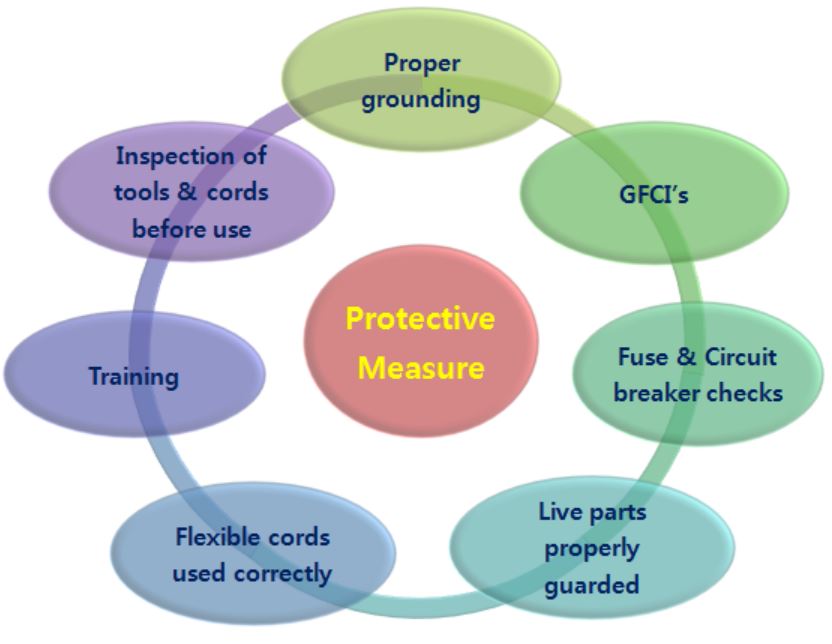
[Protective Measures]
[Closing]
눈에 보이지 않는 전기는 코끼리까지 사망에 이르게 하는 위험요인을 갖고 있습니다.

