▣ Power Plant Design Overview
The layout of the main buildings and equipment of the power plant ensures access to each building and equipment for construction and maintenance. The transformer, located at the front of the turbine building, is connected to a gas-insulated substation. Boiler combustion gases are emitted to the atmosphere via an induced draft fan. The design incorporates pollution control measures, such as electrostatic precipitators, tall chimneys, wastewater treatment facilities, anti-dust equipment, noise reduction, and nitrogen oxide reduction measures.
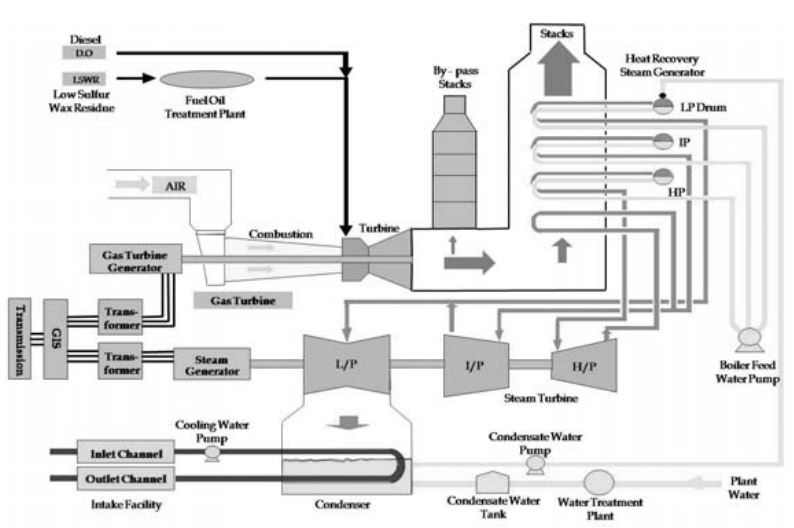
▣ Major Equipment Description
- Steam Generator
- Light oil is used as fuel for ignition and startup, while bituminous coal or heavy fuel oil (HFO) is used for normal load operation (25% or more of the maximum continuous rating).
- Turbine Generator
- The generator is a closed, cylindrical, synchronous machine with a cooling system that employs water cooling for the stator and hydrogen cooling for the rotor.
- It is a two-pole, 60Hz, three-phase hydrogen-cooled type.
▣ Main System Descriptions
- Condensate System Equipment
- The exhaust from the low-pressure turbine and the boiler main feed pump drive turbine is condensed in the condenser and collected in the condenser hot well. It is then transferred to the gland steam condenser and low-pressure feedwater heater using a condensate pump, and subsequently to the deaerator and deaerator storage tank.
- A vacuum pump is installed to maintain the vacuum state of the condenser.
- The condensate pump is vertical type, operating with one to two pumps during normal operation (one pump is a standby unit).
- Feedwater System Equipment
- The feedwater system supplies feedwater from the deaerator to the boiler economizer, comprising the deaerator and deaerator storage tank, high-pressure feedwater heater, turbine-driven main feed pump, feedwater booster pump, and a startup feed pump.
- Except for the No. 1 and No. 2 low-pressure feedwater heaters, other feedwater heaters are equipped with bleeder trip valves and motor-operated shut-off valves.
- The bleeder trip valve prevents turbine overspeed, while the motor-operated shut-off valve prevents water inflow from the heater.
- Circulating Water System Equipment
- The circulating water pump is a vertical wet-pit type installed in the intake facility area.
- Each unit has its intake facility, which consists of a trash rack, rake, and traveling screen.
- Titanium tubes, known for their excellent corrosion resistance to seawater, are primarily used in the condenser tubes.
- A tube cleaning device that injects balls into the condenser tubes is used for cleaning marine deposits.
- An air removal device is installed in the condenser to maintain vacuum within the water chamber.
- Makeup Water System
- The makeup water system demineralizes water using the pure water manufacturing facility system, stores it in a pure water storage tank, and supplies it as boiler water, laboratory water, cooling water system, and auxiliary boiler makeup water.
- The pure water treatment facility consists of an activated carbon filter, cation, anion exchangers, and mixed bed ion exchangers. The pure water is transferred to the condenser using pure water transfer pumps.
- Fuel Oil Transfer and Distribution System
- Boiler combustion fuel is transferred and stored in the fuel oil storage tank by the unloading pump of the transport ship.
- The fuel oil from the storage tank is supplied to the boiler combustion burners through a transfer pump via a day tank.
- Compressed Air System
- The compressed air system used in the power plant is divided into the instrument air system (IA System) and the service air system. The IA system delivers dry compressed air after passing through an air receiver and air dryer and is supplied to pneumatic automatic control devices and various measurement and control devices.
- Coal Handling System
- Coal unloaded at the coal-exclusive pier of the bituminous coal-fired power plant is stored in the outdoor coal yard or transported directly to the coal storage silo via a belt conveyor after passing through the pulverizer room.
- Ash Handling System
- Ash generated from the boiler is classified into fly ash and bottom ash. Fly ash is handled separately for storage or disposed of together with bottom ash in the ash disposal area.
- Fly ash is transferred from the economizer hopper, air preheater hopper, and electrostatic precipitator to the fly ash storage silo or the ash transfer tank for combined disposal with bottom ash in the ash disposal area.
▣ Power System and Plant Operation Control Methods
1) Power System
-
- Each unit’s internal power is primarily supplied from the unit’s generator output.
- During power plant startup or internal auxiliary transformer power supply interruption, power is supplied through the startup transformer.
2) Power Plant Operation Control Methods
-
- The plant adopts a centralized automatic control operation method.
- Automatic control is enabled at 25% or more of the load.
